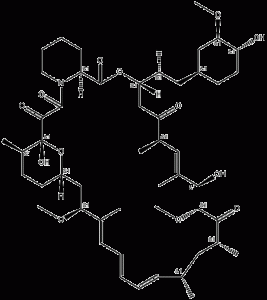
Rapamycin Is An Immunosuppressive Drug, Anti-cancer and Anti-aging
Product Detail
| Name | Rapamycin |
| CAS number | 53123-88-9 |
| Molecular formula | C51H79NO13 |
| Molecular weight | 914.19 |
| EINECS Number | 610-965-5 |
| Boiling Point | 799.83°C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.0352 |
| Storage condition | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| Form | Powder |
| Color | White |
| Packing | PE bag+Aluminum bag |
Synonyms
AY 22989;23,27-EPOXY-3H-PYRIDO(2,1-C)(1,4)OXAAZACYCLOHENTRIACONTINE;NSC-226080;RAPA;RAPAMUNE;RAPAMYCIN;RAPAMYCIN, STREPTOMYCES HYGROSCOPICUS;RPM
Pharmacological Effect
Description
Rapamycin is a macrolide antibiotic that is structurally similar to Procofol (FK506), but has a very different immunosuppressive mechanism. FK506 inhibits the proliferation of T lymphocytes from G0 phase to G1 phase, while RAPA blocks signaling through different cytokine receptors and blocks the progression of T lymphocytes and other cells from G1 phase to S phase, compared with FK506 , RAPA can block calcium-dependent and calcium-independent signaling pathways of T and B lymphocytes. University of Chicago medical researchers use commercially available oral rapamycin tablets plus grapefruit juice to treat melanoma, a common malignant tumor disease in Europe and the United States, which can greatly improve the anticancer effect of other chemotherapy drugs, thereby prolonging the survival of patients time. Studies have shown that rapamycin is easily decomposed by enzymes after entering the digestive tract, and grapefruit juice contains a large amount of furanocoumarins, which can inhibit the destructive effect of digestive tract enzymes on rapamycin. Can improve the bioavailability of rapamycin. It is said that the earliest Dutch doctors have discovered that grapefruit juice has the effect of improving the oral absorption of Shanming, and now doctors in European and American countries have applied it to rapamycin preparations.
In recent years, studies have found that the target of rapamycin (mTOR) is an intracellular kinase, and the abnormality of its conduction pathway can induce a variety of diseases. As a targeted inhibitor of mTOR, rapamycin can treat tumors closely related to this pathway, including renal cancer, lymphoma, lung cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, neuroendocrine cancer and gastric cancer. Especially in the treatment of two rare diseases, LAM (lymphangiomyomatosis) and TSC (tuberous sclerosis), the effect is more obvious, and LAM and TSC can also be regarded as tumor diseases to some extent.
Side Effect
Rapamycin (RAPA) has similar side effects to FK506. In a large number of clinical trials, its side effects were found to be dose-dependent and reversible, and RAPA at therapeutic doses has not been found to have significant nephrotoxicity and no gingival hyperplasia. The main toxic and side effects include: headache, nausea, dizziness, nosebleeds, and joint pain. Laboratory abnormalities include: thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, low hemoglobin, hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, elevated liver enzymes (SGOT, SGPT), elevated lactate dehydrogenase, hypokalemia, Hypomagnesemia, etc. Eyelid edema was recently reported with RAPA administration, and the cause of lower plasma phosphate levels is thought to be prolonged phosphate excretion from the transplanted kidney by RAPA-based immunosuppressive therapy. Like other immunosuppressants, RAPA has an increased chance of infection, with a reported tendency to increase pneumonia in particular, but the occurrence of other opportunistic infections is not significantly different from CsA.